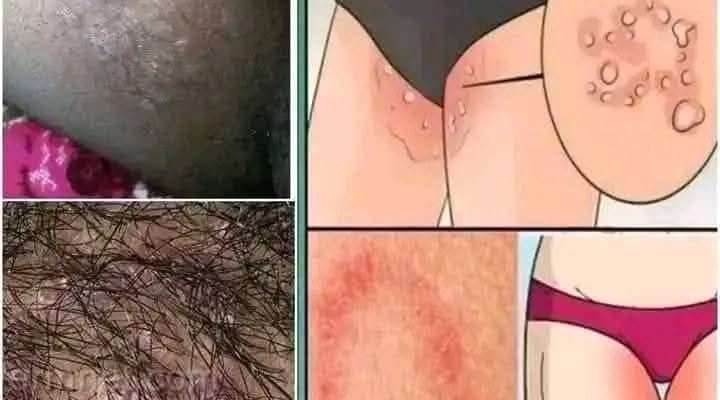
Understanding Groin Rashes: What These Skin Conditions Mean and How to Treat Them
The groin is a sensitive and often overlooked area of the body, yet it’s prone to various skin conditions due to its warmth, moisture, and friction from clothing. If you’ve noticed unusual rashes, redness, bumps, or circular patches on your inner thighs or groin area, you’re not alone. These symptoms are common and usually treatable, but understanding what they mean is key to choosing the right care.
Let’s break down what these skin changes may indicate based on the types shown in the image above.
1. Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris)
One of the most common causes of red, itchy rashes in the groin is jock itch, a fungal infection caused by dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making the inner thighs, buttocks, and genitals the perfect breeding ground — especially for athletes or those who sweat heavily.
Signs:
-
Red or pink ring-shaped rash
-
Itching, burning sensation
-
Scaly or cracked skin
-
Often starts in the groin fold and spreads outward
Treatment:
-
Over-the-counter antifungal creams (e.g., clotrimazole, terbinafine)
-
Keeping the area clean and dry
-
Wearing loose, breathable clothing
-
Avoid sharing towels or underwear
2. Folliculitis
Folliculitis is an infection or inflammation of the hair follicles, often caused by shaving, friction, or bacterial growth (commonly Staphylococcus aureus). In the groin area, it may look like red pimples or white-headed bumps clustered around hair follicles.
Signs:
-
Small red or pus-filled bumps
-
Itching or tenderness
-
Can occur after shaving or waxing
-
Sometimes mistaken for acne
Treatment:
-
Gentle cleansing with antibacterial soap
-
Warm compresses
-
Avoid shaving the area until healed
-
In severe cases, a doctor may prescribe antibiotics
3. Intertrigo
Intertrigo is a rash that forms in skin folds where moisture and friction are high. In the groin area, especially in overweight individuals or those with excessive sweating, intertrigo can cause discomfort and is often secondarily infected with bacteria or yeast.
Signs:
-
Red, inflamed skin in folds
-
Raw, painful patches
-
Bad odor or oozing in severe cases
Treatment:
-
Keep the area dry and clean
-
Apply barrier creams (like zinc oxide)
-
Use antifungal or antibacterial creams if needed
-
Weight management and breathable clothing can help prevent recurrence
4. Yeast Infections (Candidiasis)
A yeast infection in the groin is more common than many realize, especially in women, but men can also be affected. Caused by an overgrowth of Candida albicans, this infection thrives in warm, moist conditions.
Signs:
-
Red, itchy rash with white patches or discharge
-
Burning sensation
-
In women, it may spread from the vaginal area to the inner thighs
Treatment:
-
Antifungal creams or oral medication (e.g., fluconazole)
-
Avoid using scented soaps or tight clothing
-
Maintain good hygiene
5. Contact Dermatitis
Sometimes, the rash is not due to an infection but a reaction to something your skin came into contact with — like a new soap, detergent, or fabric.
Signs:
-
Itchy, red rash that may blister or peel
-
Occurs shortly after contact with an irritant or allergen
-
May be limited to areas touching the substance
Treatment:
-
Identify and avoid the irritant
-
Use mild topical corticosteroids
-
Moisturize the area to aid healing
When to See a Doctor
While many groin rashes can be treated at home, certain signs indicate the need for medical attention:
-
Rash is spreading rapidly
-
Fever accompanies the rash
-
Severe pain or pus discharge
-
No improvement after 1–2 weeks of treatment
-
Rash returns frequently
A healthcare provider can do a skin scraping, culture, or biopsy if needed to diagnose the exact cause.
Prevention Tips
-
Stay Dry: After bathing or sweating, make sure the groin is completely dry before dressing.
-
Wear Loose Clothing: Choose cotton underwear and avoid tight pants that cause chafing.
-
Practice Good Hygiene: Daily showers and changing underwear regularly are key.
-
Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Towels, razors, or clothing can spread infections.
-
Trim Carefully: If shaving, use clean razors and consider trimming instead to avoid folliculitis.
Final Thoughts
Groin rashes can be uncomfortable, embarrassing, and persistent, but they’re usually manageable with the right approach. The key is recognizing the type of condition early and taking action — whether through home care or professional treatment.
Remember, there’s no shame in seeking help for skin issues in private areas. Your comfort and health are worth the attention. If you’re unsure about a rash or if it worsens, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider.